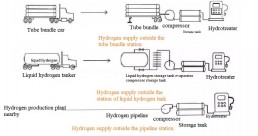
There is no hydrogen production unit in the external hydrogen supply hydrogen refueling station. Hydrogen is transported from the hydrogen plant to the hydrogen refueling station through long tube trailers, liquid hydrogen tankers or hydrogen pipelines, compressed by the compressor and transported to the high-pressure hydrogen storage bottle for storage, and finally filled into fuel cell vehicles through the hydrogen dispenser.
According to different hydrogen storage modes, it can be further divided into high-pressure gas hydrogen station and liquid hydrogen station,About 30% of the world’s liquid hydrogen storage and transportation stations are hydrogen refueling stations, which are mainly distributed in the United States and Japan. At present, China is all high pressure gas hydrogen stations.Compared with the gas hydrogen storage and transportation, the liquid hydrogen storage and transportation hydrogenation station occupies a smaller area and has a larger storage capacity, but it is also more difficult to construct, which is suitable for large-scale hydrogenation.
Fig. 1 Technical Route of External Hydrogen Supply and Hydrogenation Station
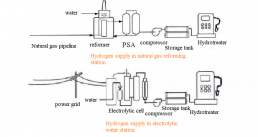
The internal hydrogen production and hydrogenation station is equipped with a hydrogen production system. The hydrogen production technologies include hydrogen production by electrolysis of water, hydrogen production by natural gas reforming, and hydrogen production by renewable energy. The hydrogen produced in the station generally needs to be purified, dried, and then compressed, stored, and injected.Among them, electrolytic water hydrogen production and natural gas reforming hydrogen production technologies are most widely used in the station hydrogen production and hydrogenation stations because of the ease of equipment installation and high degree of automation, and the natural gas reforming technology can be developed based on the construction of natural gas infrastructure. The European hydrogen production and hydrogenation stations mainly use these two hydrogen production methods.
Fig. 2 Technical route of internal hydrogen production and hydrogenation station
According to different hydrogen supply pressure levels, the hydrogen refueling station is divided into two types of hydrogen supply pressure: 35MPa and 70MPa.
Most foreign markets use 70 MPa,Restricted by the development of existing compressor and hydrogen storage bottle technologies, most domestic hydrogen refueling stations use 35 MPa.When 35 MPa pressure is used for hydrogen supply, the working pressure of the hydrogen compressor is 45 MPa, and the working pressure of the high-pressure hydrogen storage cylinder is 45 MPa;When 70 MPa pressure is used for hydrogen supply, the working pressure of the hydrogen compressor is 98 MPa, and the working pressure of the high-pressure hydrogen storage cylinder is 87.5 MPa.
On the basis of the original or new gas station and gas station, add hydrogenation functional facilities to make the station have multiple functions such as refueling, gas refueling, hydrogenation, etc.According to the Technical Code for Hydrogenation Station (GB 50516-2010), the hydrogen refueling station can be built in a single station, requiring relocation and high input cost;The oil hydrogen hybrid station is the development direction of the future hydrogen refueling station, which can also avoid the need for more space and time for electric vehicle charging.
Glacier coolant provides customers with coolant to ensure that the temperature is kept at – 40 ° C when hydrogen is injected, alleviate the temperature rise of pressure drop, and is widely used in hydrogen refueling stations.Through long-term research, our company has invented glacier coolant products and applied for national patents.He has successively invented “M3 super film rust prevention” technology, “Modify2000 composite modification” technology and “Box7 all-around test”.The problems such as corrosion of equipment, narrow temperature range and potential safety hazards caused by salt water, ethylene glycol and dichloromethane, which are substitutes of traditional coolant, have been solved.In addition to hydrogen refueling stations, they are also widely used as industrial low temperature load coolant, pharmaceutical high and low temperature load coolant, industrial antifreeze, central air-conditioning antifreeze, solar antifreeze, automobile antifreeze, laser antifreeze, etc.
