Chemical Raw Material
Chemical Raw Material
Urea
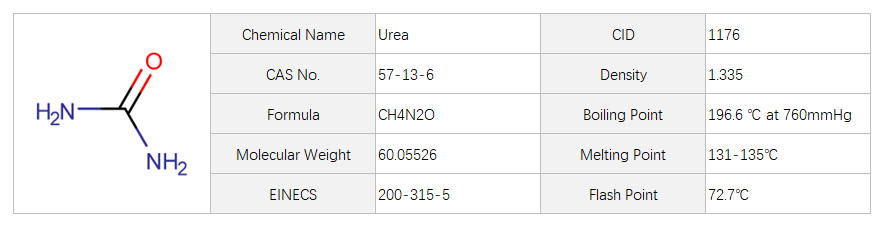
Urea is a stable highly water-soluble compoundof high nitrogen content (47%), with good storageproperties that make it the most commonly used nitrogenfertilizer.Used in fertilizers and animal feeds, as a fungicide, in the manufacture of resins and plastics, as a stabilizer in explosives and in medicines, and others. Urea is used to protect against frost and is used in some pesticides as an inert ingredient as a stabilizer, as an inhibitor and as an intensifier for herbicides.
Calcium chloride
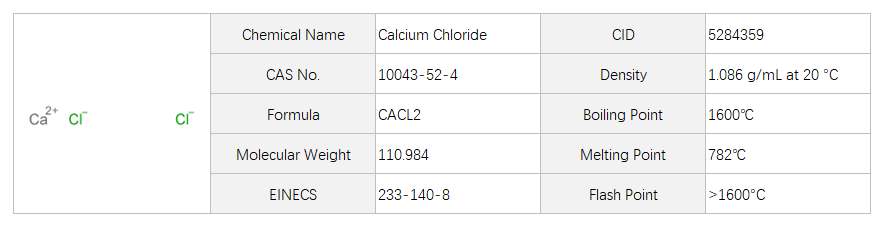
Calcium chloride is a white crystalline solid that appears as a colorless to white powder. It has a strong, salty taste and is odorless. The basic structure of calcium chloride consists of one calcium atom bonded to two chlorine atoms. Calcium chloride is commonly used as a de-icing agent to melt ice and snow on roads, sidewalks, and other surfaces. Its mechanism of action involves lowering the freezing point of water, which helps prevent the formation of ice. Calcium chloride also provides traction on slippery surfaces.
Melamine
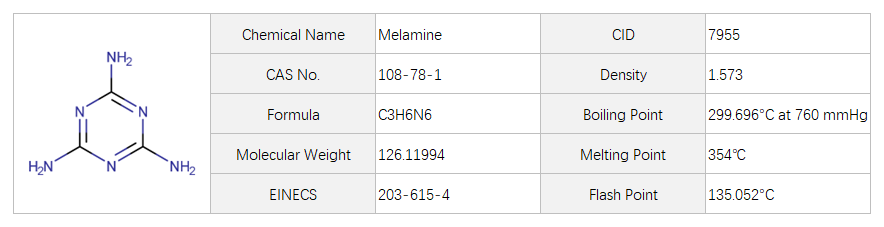
White Solid Melamine is a white crystalline solidChEBI: A trimer of cyanamide, with a 1,3,5-triazine skeleton. A white solid organic compound whose molecules consist of a sixmembered heterocyclic ring of alternate carbon and nitrogen atoms with three amino groups attached to the carbons. Condensation polymerization with methanal or other aldehydes produces melamine resins, which are important thermosetting plastics. melamine: A white crystalline compound.
Sodium Hydroxide
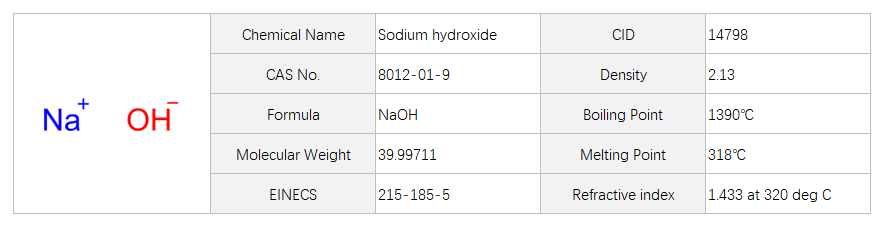
Sodium hydroxide, with the chemical formula NaOH, has the CAS number 8012-01-9. It is a white solid with no distinct odor. Sodium hydroxide is an inorganic compound that consists of a sodium cation (Na+) and a hydroxide anion (OH-). It is highly soluble in water, with the ability to dissolve in large amounts.Sodium hydroxide is widely used in the chemical industry for various purposes. It is commonly used as a strong base in the production of chemicals such as detergents, soaps, and paper. The mechanism of action in chemical manufacturing involves its ability to react with acidic compounds, neutralizing them and forming salts.
Citric Acid
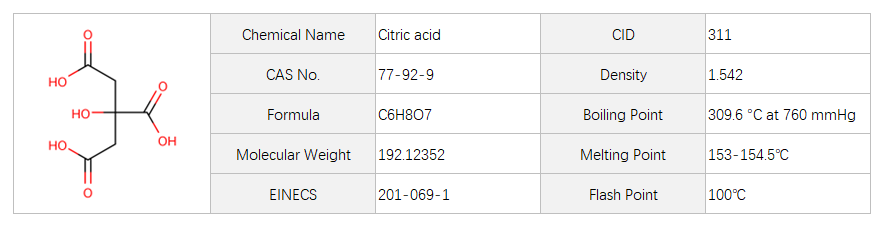
Citric acid (CAS 77-92-9) is a white crystalline powder that is commonly used in various industries. Its basic structure consists of a tricarboxylic acid with the chemical formula C6H8O7. It is highly soluble in water, resulting in a clear solution. The physical appearance of citric acid is that of a fine white powder with a crystalline texture.Citric acid is widely used in the food and beverage industry as a flavor enhancer, preservative, and acidulant. Its mechanism of action involves enhancing the tartness and acidity of food products, as well as inhibiting the growth of bacteria and fungi.
Propylene Glycol
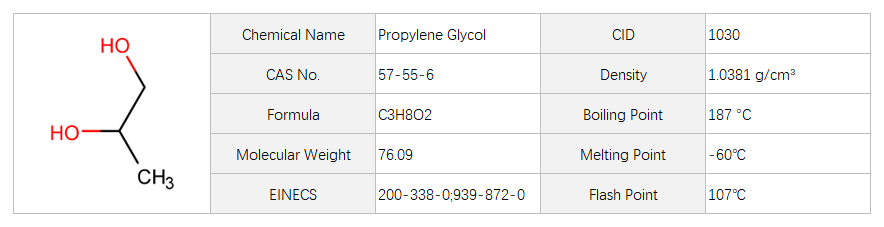
Propylene glycol (CAS 57-55-6) is a colorless, odorless, and viscous liquid. It has a basic structure consisting of two hydroxyl groups attached to a propylene backbone. This chemical is highly soluble in water, making it miscible in all proportions. It also exhibits low volatility and a low freezing point, which contributes to its wide range of applications. Propylene glycol is commonly used as a solvent, humectant, and emulsifier in various industries.
Propylene glycol is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry as a solvent and excipient. It helps to dissolve and stabilize active pharmaceutical ingredients in medications, ensuring their uniform distribution. The mechanism of action involves enhancing the solubility and bioavailability of drugs.
Potassium Formate
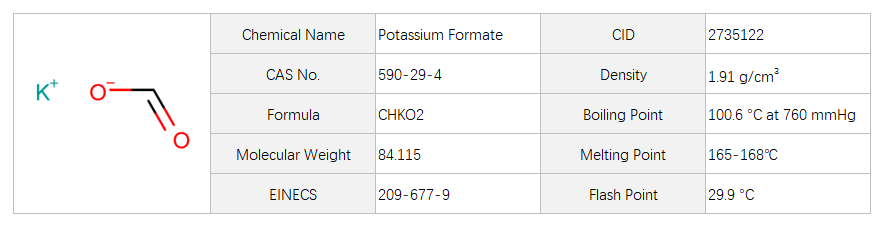
Potassium formate, with the chemical formula CHKO2, has the CAS number 590-29-4. It appears as a white crystalline solid with a slight odor. The basic structure of potassium formate consists of a potassium cation (K+) and a formate anion (HCOO-). This compound is highly soluble in water.
Potassium formate is commonly used in the oil and gas industry as a drilling fluid additive. Its purpose in this field is to control the rheological properties of the drilling fluid and prevent clay swelling. The mechanism of action involves the formation of a thin, impermeable filter cake on the wellbore walls, which helps to maintain well stability and prevent fluid loss.
Xanthan Gum
Xanthan gum is a polysaccharide produced by the bacterium Xanthomonas campestris. Xanthan gum appears as a white to cream-colored powder with a faint, characteristic odor. Its basic structure consists of a backbone of glucose units with side chains of mannose and glucuronic acid. This compound is soluble in water and forms a viscous gel when hydrated.
Xanthan gum is considered safe for consumption and is commonly used as a food additive and thickening agent. It is also used in various industries, including cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and oil drilling.

